Biodegradable silica based platform for antiviral drug delivery
Speaker: Lasse Leino, CEO, DelSiTech Ltd

Introduction to DelSiTech Silica Matrix technology Case study: development of a prototype formulation for HIV bNAb delivery. DelSiTech – biodegradable, amorphous, non-porous silica-based drug delivery.
- Develops LA injectables (SC,IM) that enable controlled release for days to months.
- Silica matrix technology is applicable to a large range of drugs – small molecules, peptides, proteins, oligonucleotides and vaccines.
- Multiple ongoing drug development projects for antiviral therapy (in-house and with external partners).
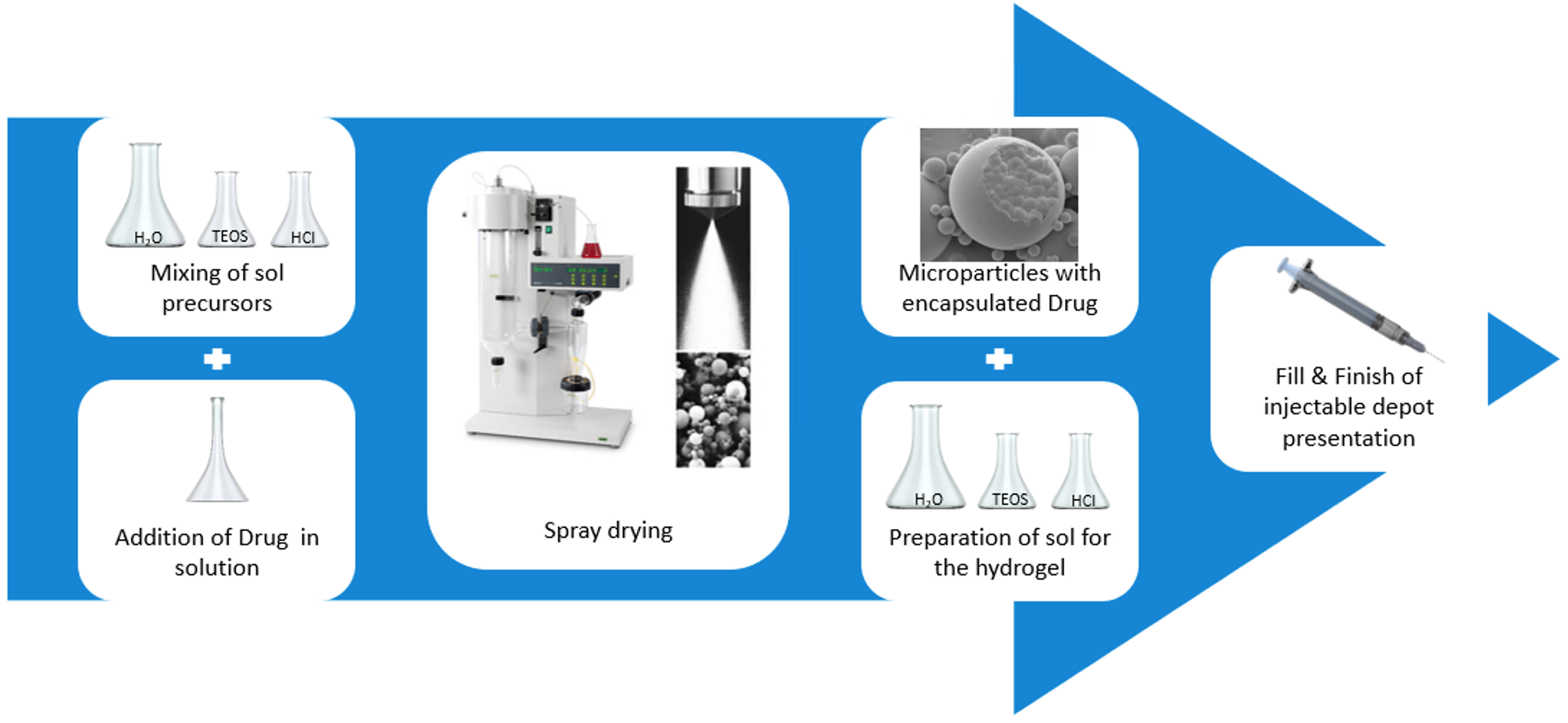
Introduction to DelSiTech Silica matrix technology.
- Non-porous silica microparticles containing an encapsulated drug are combined with silica hydrogel forming an easily injectable silica-silica composite depot formulation.
- SiO2-based biomaterial is non-porous and fully biodegradable for durable controlled release.
- Simple manufacturing process yields ready-to-use injectables.
DST1308 is the first-in-house and first-in-class supergeneric/505(b)(2) drug product for chronic hepatitis B virus treatment – FIH studies to begin early in 2024.
- Entecavir-based Q3M SC injection.
- Product protected by a global patent up to 2036 – several recent publications on the technology.
Silica matrix for LA HIV bNAb delivery (in collaboration with the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation) – preclinical studies indicate bNAb release for 4 months and the silica matrix protects the Ab for many months inside living tissue.
- Prototype depot formulation (#05D) developed for bNAb PGT-121.
- PGT-121 was fully encapsulated in silica microparticles at 25% payload and formulated into silica hydrogel for an injectable product (25G needle).
- In-house, in-vitro dissolution tests predict 5-month release of PCT-121 and full biodegradation of the silica matrix at 5 months in vivo with no burst release.
- Pre-clinical studies of single-dose SC PGT-121 in female SCID transgenic mice – in silica depot #05D vs saline bolus formulation.
- Assessed PGT-121 serum concentrations up to day 125 (depot) and day 28 (bolus) via HIV-1 neutralization assay.
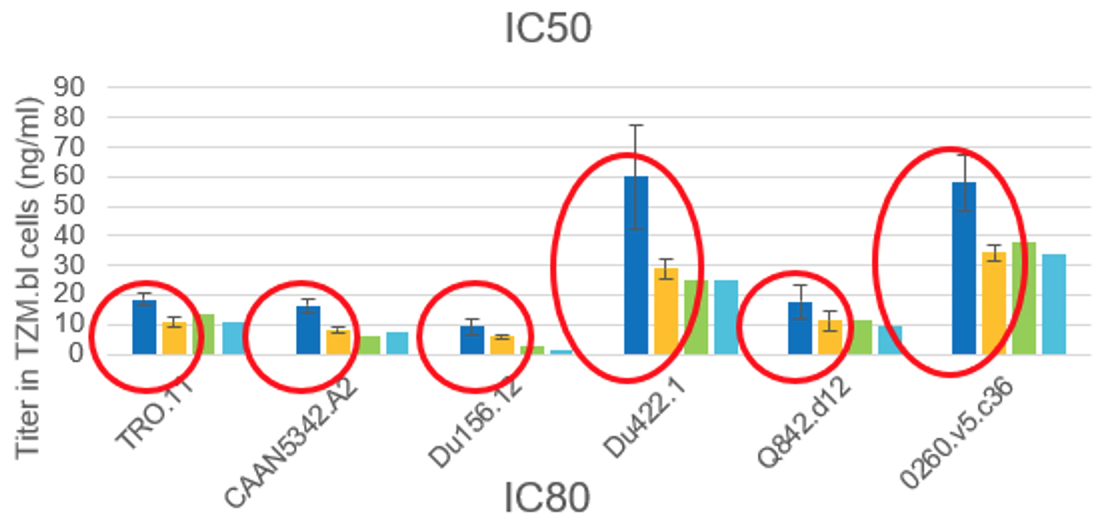
- Analyzed PGT-121 depot remnant collected from sacrificed animals: SiO2 and PGT-121 content; biological activity of remaining PGT-121 (HIV-1 neutralization assay); and binding activity (ELISA).
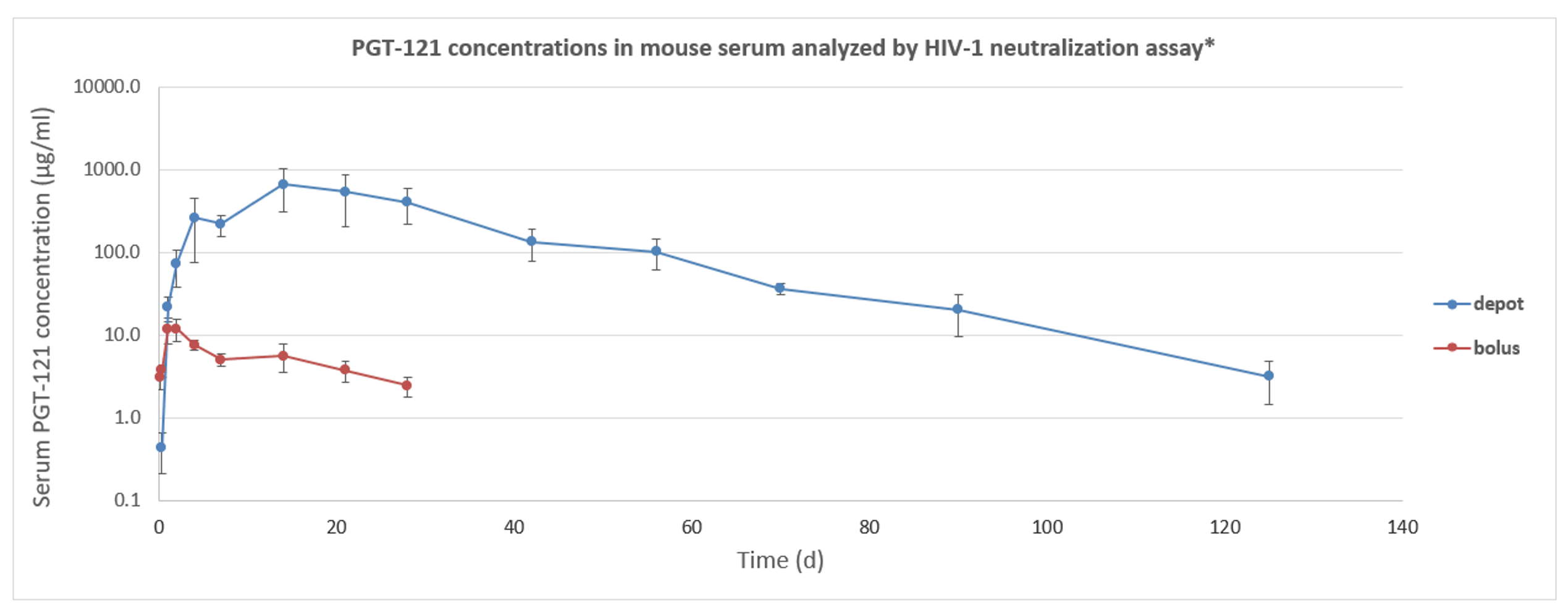
- PK – controlled release of PGT-121 up to day 40, followed by an elimination phase yielding serum exposure up to day 125 (half-life similar to bolus injection); no burst release.
- Depot remnants collected at day 90 – PGT-121 from dissolved remnant retained full biological activity compared to samples of PGT-121 stock solution.
Conclusions
- DelSiTech Silica Matrix technology offers an alternative to develop antiviral controlled-release products – small molecules and complex biologics.
- bNAb PGT-121 was successfully encapsulated and formulated at high payload (25%) in a silica-silica composite formulation.
- PK study in transgenic SCID mice showed controlled release of biologically active PGT-121 for at least 4 months after a single injection of PGT-121 silica depot formulation.
- PGT-121 retains full biological activity for at least 3 months encapsulated in the silica matrix within a living tissue.
